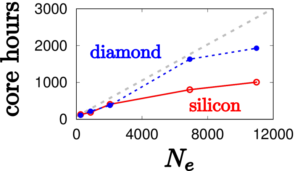
Scaling
For a set of molecules, nanocrystals and solids, stochastic GW demonstrate a near-linear scaling of total CPU time with number of electrons. This linear scaling is preserved if fragment stochastic resolution of identity is used, as in the following examples.
Parallelization
In stochasticGW, self-energies are averaged over independent stochastic orbitals, thus allowing for efficient and natural parallelization where each processor performs its own independent calculation.
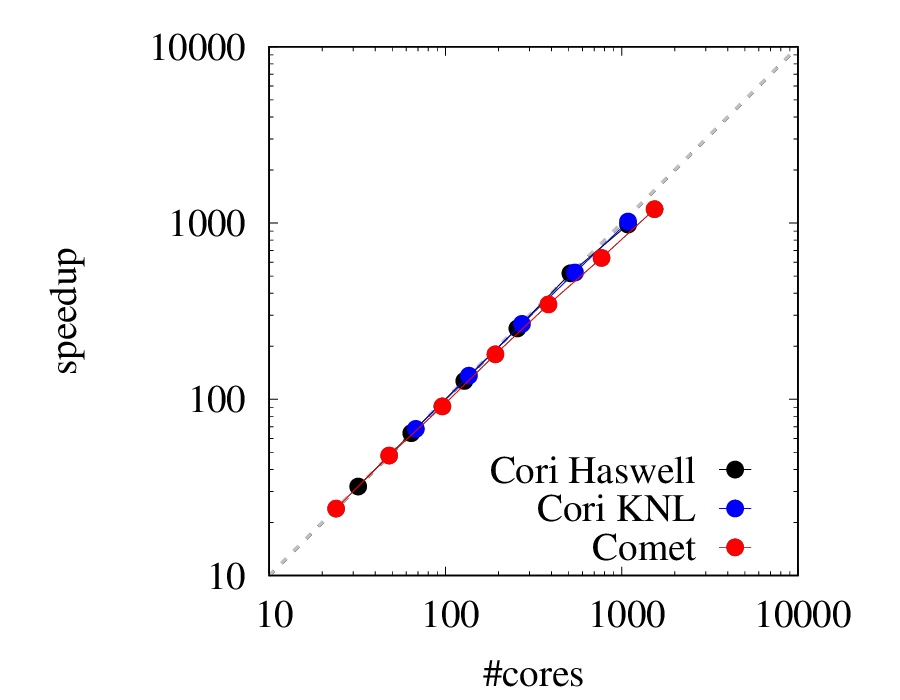
Scaling of stochasticGW on three different supercomputers
Efficiency of parallelization is about 90% even when thousands or cores are used.